Exponential growth of Smartphones has opened newer avenues for enterprises to integrate them into mainstream computing. Enterprises across all industry verticals are embracing mobility at a rapid pace.
According to Gartner’s report on Market Insight 2012, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), the rapid ascent of enterprise application stores, and the high expectations customers have of continual mobile app usability and performance improvements are just three of many factors driving mobility growth.
Enterprise applications that were initially available as web applications are now being ported to mobile devices. Enterprises are now deploying mobile applications in empowering workforces in areas like Sales, Supply Chain, Field Support and Shop Floor.
Mobile testing is quickly becoming a necessity as more and more businesses are embracing mobility. Mobile apps reflects the face of the enterprise, bad quality mobile apps can severely affect the reputation of the overall company. Even smaller issues can negatively impact the brand. For example, according to research cited by Aberdeen senior research analyst Jim Rapoza, 7% of users abandon applications after just one second of delay in performance. 11% abandon at two seconds, 18% at three, 25% at four and 50% at five seconds.
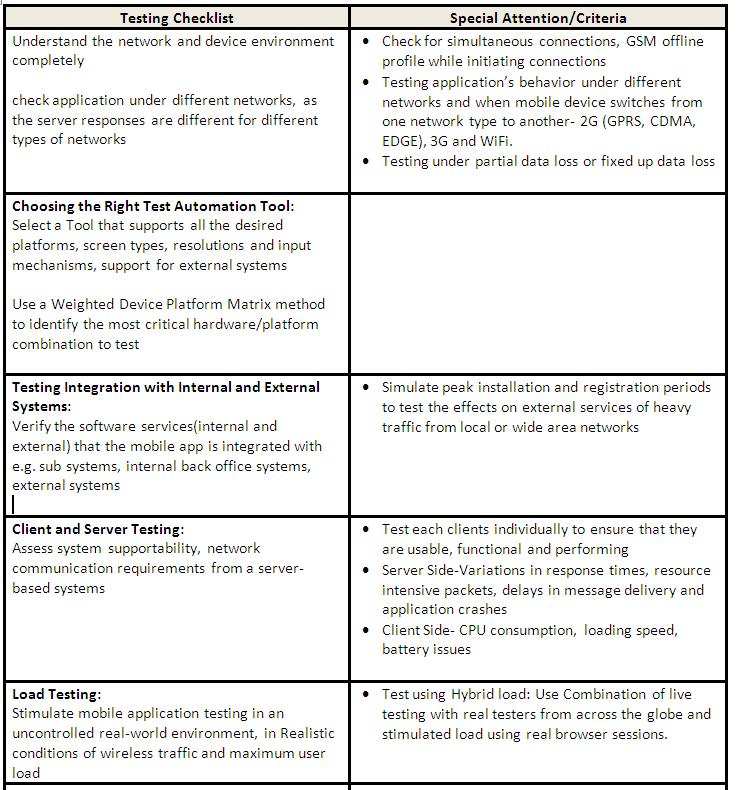
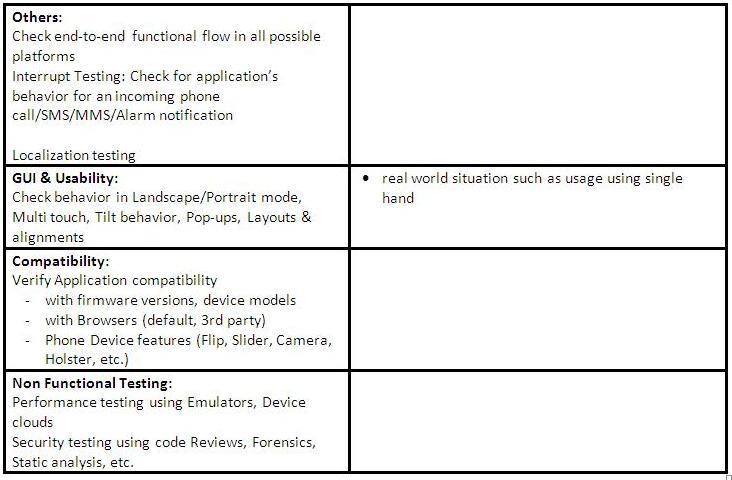
In Mobile application testing, there are unique challenges that are encountered like device and OS fragmentation, browser compatibility, UI compatibility, differences in the graphics and screen density of various devices. There are various forms of bugs that affect mobile apps testing including minor flaws related to incoming calls, power cycles, low signal strength, form factors variations, bandwidth issues, network speeds, recording user actions and input errors.
The complexity of testing mobile devices is that there is code on mobile devices, especially in business apps, code runs on several servers and in backend data centers. The system must be active to test the code on mobile devices. Setting up multiple infrastructures to test on mobile devices is an expensive proposition that customers would not prefer. The technique is to isolate the different tiers of applications and stimulate a whole data center running. The Test Engineer can virtualize and stimulate, allowing him to concentrate only on the mobile device and forget about all the backend stuff.
Automation tools available for testing:
Mainly mobile testing is done manually on actual devices. Some of the following tools are available in to test the functionality as well as usability of application.
– Robotium for Android
– Testquest, try, and digia for Symbian
– FoneMonkey for IPhones
– Memory sweep for IPhone
– Other tools: eggplant, VNC Robot, Hopper and TestQuest
Performance/load and stress testing tools
– Recent announcement by MicroFocus about SilkPerformer 9.0 (2012) supports Mobile Web & Native apps testing on iOS, Android & BB platforms
– HP LoadRunner supports mobile web & native apps testing on iOS, Android, BB & WM platforms
– NeoLoad supports mobile web & native mobile apps
– JMeter supports mobile web app testing on simulators
– IBM Rational Performance Tester (RPT) supports mobile web app testing as well
- How can a mobile application lower your motor insurance premium and improve safety? - November 18, 2015
- Aspire’s Mobile CoE and it’s focus on Xamarin - October 15, 2015
- Dalvik to ART, Why a change of runtime in Android Lollipop? - January 30, 2015






Comments