SecOps, or Security Operations, is critical in safeguarding a business’s digital assets and maintaining its online integrity. The rise of cybersecurity threats, ranging from data breaches to sophisticated cyber-attacks, has made SecOps tools essential for businesses of all sizes. These tools, including intrusion detection systems, security information and event management (SIEM) software, and vulnerability scanners, provide real-time monitoring, incident response, and threat detection and response capabilities. By integrating these tools into their infrastructure, businesses can proactively identify and address security threats, ensure compliance and adherence to regulatory standards, and protect sensitive data. This fortifies their cyber defences and helps maintain customer trust and business reputation in an increasingly digital world.
SecOps Tools – Categories and Features
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
● Real-Time Visibility: Provides real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
● Event Correlation: Identifies patterns and correlations among different security events.
● Alerting and Reporting: Automates alerting processes and generates detailed security reports.
● Forensic Analysis: Helps in investigating and analyzing past security incidents to prevent future breaches.
Vulnerability Management Tools
● Automated Scanning: Regularly scans systems for known vulnerabilities.
● Risk Assessment: Assesses the potential impact and risk of identified vulnerabilities.
● Patch Management: Facilitates the timely patching of vulnerabilities.
● Compliance Reporting: Helps maintain compliance with various security standards and regulations.
Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP)
● Malware Prevention: Offers protection against various forms of malware.
● Behavioral Monitoring: Monitors and analyzes the behavior of devices to detect anomalies.
● Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevents sensitive data from leaving the organization unauthorized.
● Device Control: Manages external devices to prevent potential security risks.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
● User Authentication: Only authenticated users can access certain resources.
● Access Control: Manages user permissions and ensures appropriate access levels.
● Multi-factor Authentication: Offers an additional security layer beyond just passwords.
● User Activity Monitoring: Tracks user activities to detect and prevent potential insider threats.
Network Security Tools
● Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Monitors network traffic to detect and prevent attacks.
● Firewalls: Controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
● Virtual Private Network (VPN): Ensures secure remote access to the network.
● Network Segmentation: Separates network segments to contain breaches and limit access.
Cloud Security Tools
● Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): Mediate between cloud service providers and users to enforce security policies.
● Configuration Management: Monitors and manages cloud infrastructure configurations.
● Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP): Offers security for cloud workloads, including serverless, containers, and VMs.
● Cloud Data Loss Prevention: Focuses on preventing data loss in the cloud environment.
Compliance Management Tools
● Regulatory Compliance Tracking: Helps organizations stay compliant with various industry-specific regulations.
● Audit Trail Management: Maintains records of compliance-related activities for auditing purposes.
● Policy Management: Aids in developing and managing security policies.
DevSecOps Tools
● Automated Security Testing: Integrates security testing into the software development process.
● Code Analysis Tools: Scans source code for potential security vulnerabilities.
● Container Security: Provides security for containerized applications.
Threat Intelligence Platforms
● Global Threat Data: Aggregates and analyzes data on global security threats.
● Contextual Intelligence: Offers context around threats to aid in decision-making.
● Integration with Other Tools: Feeds valuable threat intelligence into other SecOps tools for a coordinated response.
SecOps tools are vital for contemporary cybersecurity, automating tasks to let teams focus on strategic defense against evolving threats. These tools safeguard digital assets, intellectual property, and sensitive data, essential for maintaining business trust and competitiveness. SecOps ensures business continuity and customer confidence by preventing cyber-attacks and minimizing financial losses. Compliance with cybersecurity regulations and gaining a competitive edge in data-sensitive industries further underline their strategic importance.
Four available options stand out: ServiceNow SecOps module, Qualys, Elastic Security, and Rapid7. Each offers unique features and capabilities, catering to different business needs and security requirements. The features, pros, and cons of each of these should help you decide which tool is best for your business.
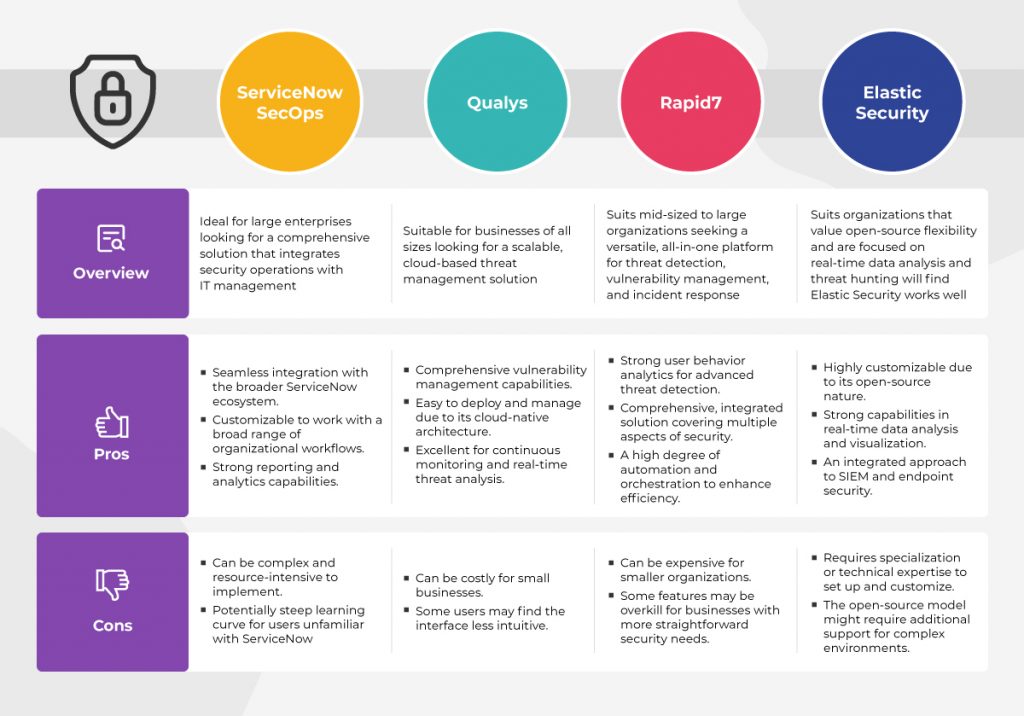
ServiceNow SecOps
Key Features:
● Incident Response and Vulnerability Response: Streamlines identifying and responding to security incidents and vulnerabilities
● Integration with IT Operations: Seamlessly integrates with other ServiceNow modules, enhancing cross-functional collaboration between IT and security teams.
● Customizable Workflow Automation: Automates routine tasks and customizes workflows for specific organizational needs.
The ServiceNow SecOps module is ideal for large enterprises looking for a comprehensive solution that integrates security operations with IT management.
Pros:
● Seamless integration with the broader ServiceNow ecosystem.
● Customizable to work with a broad range of organizational workflows.
● Strong reporting and analytics capabilities.
Cons:
● Can be complex and resource-intensive to implement.
● Potentially steep learning curve for users unfamiliar with ServiceNow.
Qualys
Key Features:
● Cloud-Based Platform: Offers a scalable, cloud-based solution for vulnerability management, compliance, and web application security.
● Continuous Monitoring: Provides continuous monitoring and automatic updates for real-time threat intelligence.
● Global AssetView: Delivers a holistic view of all IT assets, making managing and securing them easier.
Qualys is suitable for businesses of all sizes looking for a scalable, cloud-based threat management solution.
Pros:
● Comprehensive vulnerability management capabilities.
● Easy to deploy and manage due to its cloud-native architecture.
● Excellent for continuous monitoring and real-time threat analysis.
Cons:
● Can be costly for small businesses.
● Some users may find the interface less intuitive.
Elastic Security
Key Features:
● Open-Source Foundation: Built on the robust, open-source Elasticsearch stack.
● Real-Time Analytics: Offers powerful, real-time analytics and search capabilities.
● Integrated SIEM and Endpoint Security: Combines SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) with endpoint security for a more holistic approach.
Organizations that value open-source flexibility and are focused on real-time data analysis and threat hunting will find Elastic Security works well.
Pros:
● Highly customizable due to its open-source nature.
● Strong capabilities in real-time data analysis and visualization.
● An integrated approach to SIEM and endpoint security.
Cons:
● Requires specialization or technical expertise to set up and customize.
● The open-source model might require additional support for complex environments.
Rapid7
Key Features:
● Insight Platform: Offers a cloud-based platform that combines threat management, application security, and incident detection and response.
● User Behavior Analytics: Leverages user behavior analytics to detect and respond to anomalies
● Automation and Orchestration: Provides advanced automation and orchestration capabilities for efficient threat detection and response.
Rapid7 suits mid-sized to large organizations seeking a versatile, all-in-one platform for threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident response.
Pros:
● Strong user behavior analytics for advanced threat detection.
● Comprehensive, integrated solution covering multiple aspects of security.
● A high degree of automation and orchestration to enhance efficiency.
Cons:
● Can be expensive for smaller organizations.
● Some features may be overkill for businesses with more straightforward security needs.
SecOps Tools: Making the Right Choice
Selecting the best SecOps tool for your business depends on various factors, such as the size of your organization, specific security needs, technical expertise, and budget. A ServiceNow SecOps implementation is ideal for enterprises needing extensive ITSM integration, while Qualys excels in cloud-based vulnerability management. Elastic Security is suited for those prioritizing real-time data analysis and open-source flexibility, whereas Rapid7 offers an integrated, behavior-analytics-focused solution.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by your business objectives, the nature of your digital assets, and the specific threats you aim to mitigate. A thorough evaluation, including demos and trials, can significantly aid in making an informed choice. Remember, the best tool is not just about features; it’s about how well it aligns with your organization’s unique security posture and operational dynamics.
Follow AspireSystems ServiceNow to stay informed with detailed insights and timely updates!.
- How to improve security and compliance in retail IT environments - August 23, 2024
- Top 5 Cybersecurity Threats Faced by Retailers - August 22, 2024
- How Managed Services Can Solve Compliance Issues for Retailers - August 20, 2024







Comments